ML04 | 线性回归训练
Javascript玩转机器学习04
线性回归是什么
- 一种统计分析方法
- 用于确定两种(或以上)变量间相互依赖的定量关系
- eg.身高体重预测(两种变量)、房价预测(多变量)
操作步骤
- 准备、可视化:训练数据
- 用TensorFlow.js的API构建一个简单的神经网络
- 训练模型 并 预测
前置条件
- 最新版本chrome
- 代码编辑器(eg.VSCODE
- 基础的前端、神经网络知识
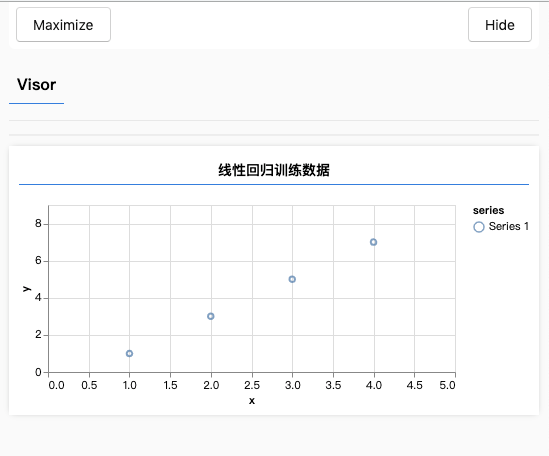
准备、可视化:训练数据(实操)
- 准备线性回归训练数据(特征、标签)
- 使用tfvis可视化训练数据(tfvis是一个神经网络可视化库)
<!-- linear-regression/index.html-->
<script src="script.js"></script>// linear-regression/script.js
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
window.onload = () => {
const xs = [1, 2, 3, 4]; //input
const ys = [1, 3, 5, 7]; //output
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "线性回归训练数据" },
{ values: xs.map((x, i) => ({ x, y: ys[i] })) },
{ xAxisDomain: [0, 5], yAxisDomain: [0, 9] },
);
};-- bash
parcel li*/*.html可视化效果
定义单个神经元的神经网络模型
- 初始化一个神经网络模型(model)
- 为模型添加层(layer)
- 设计层的神经元个数和inputShape
import * as tfjs from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
window.onload = () => {
const xs = [1, 2, 3, 4]; //input
const ys = [1, 3, 5, 7]; //output
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "线性回归训练数据" },
{ values: xs.map((x, i) => ({x, y:ys[i]})) },
{xAxisDomain:[0,5],yAxisDomain:[0,9]}
);
const model = sf.sequential(); //创造一个连续模型
model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:1,inputShape:[1]})); //添加一个全连接层(点乘权重+偏置)
};
损失函数:均方误差(MSE-MeanSquaredError)
-
利用google ML playground 理解损失函数与均方误差:
-
损失函数用于计算预测值与实际值差距
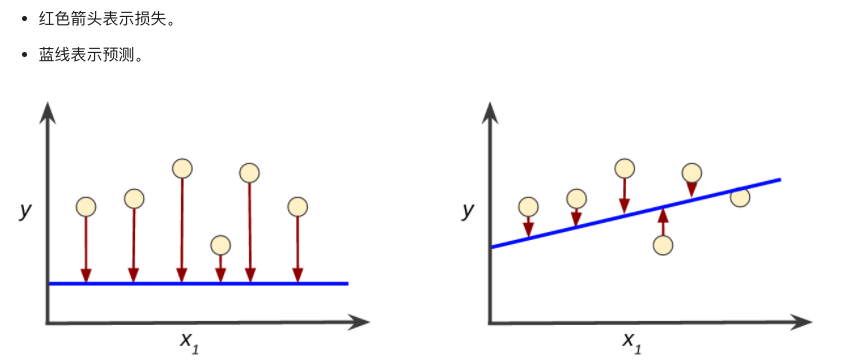
- 均方误差(meanSquaredError)是一种损失函数

- 在TensorFlow.js中设置损失函数
import * as tfjs from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
window.onload = () => {
const xs = [1, 2, 3, 4]; //input
const ys = [1, 3, 5, 7]; //output
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "线性回归训练数据" },
{ values: xs.map((x, i) => ({x, y:ys[i]})) },
{xAxisDomain:[0,5],yAxisDomain:[0,9]}
);
const model = sf.sequential(); //创造一个连续模型
model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:1,inputShape:[1]})); //添加一个全连接层(点乘权重+偏置)
model.compile({loss:tf.losses.meanSquaredError}) //设置损失函数为均方误差MSE
};优化器:随即梯度下降(SGD)
-
利用google ML playground 理解优化器与随机梯度下降:
-
迭代试错:
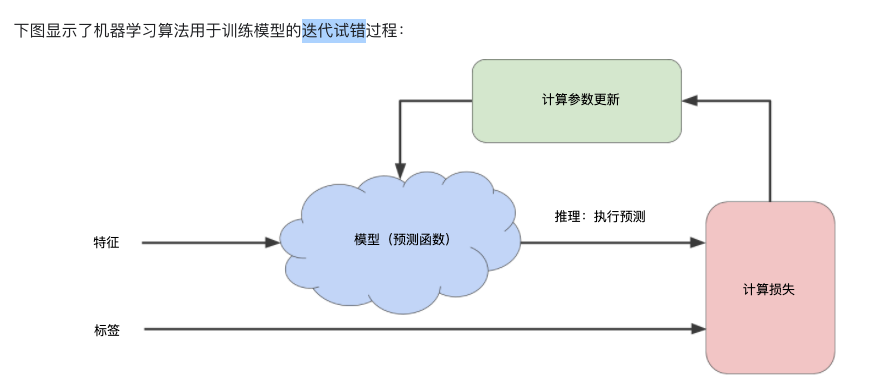
- 梯度下降法:
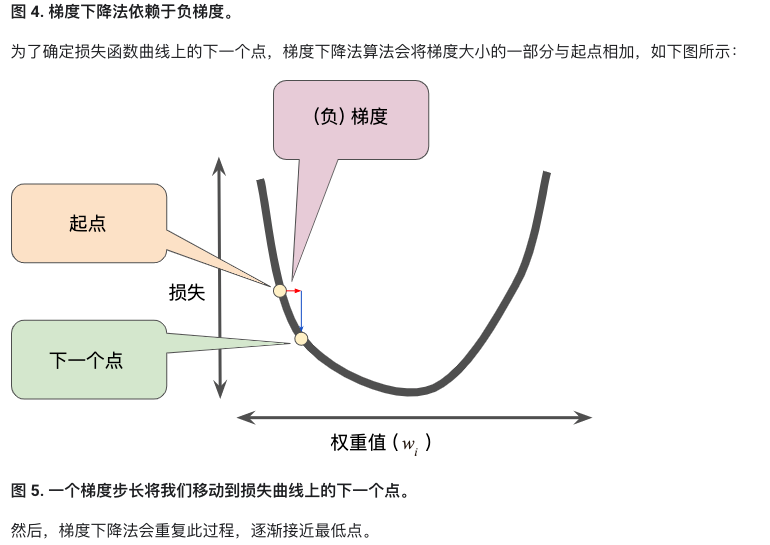
- SGD

- 在TensorFlow.js中设置优化器
import * as tfjs from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
window.onload = () => {
const xs = [1, 2, 3, 4]; //input
const ys = [1, 3, 5, 7]; //output
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "线性回归训练数据" },
{ values: xs.map((x, i) => ({x, y:ys[i]})) },
{xAxisDomain:[0,5],yAxisDomain:[0,9]}
);
const model = sf.sequential(); //创造一个连续模型
model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:1,inputShape:[1]})); //添加一个全连接层(点乘权重+偏置)
model.compile({loss:tf.losses.meanSquaredError,optimizer:tf.train.sgd}); //设置:损失函数为均方误差MSE,优化器为随机梯度下降SGD
};训练模型并可视化训练过程
- 将训练数据转为tensor
- 训练模型
- 用tfvis可视化训练过程
import * as tf from "@tensorflow/tfjs";
import * as tfvis from "@tensorflow/tfjs-vis";
window.onload = async () => {
const xs = [1, 2, 3, 4]; //input
const ys = [1, 3, 5, 7]; //output
tfvis.render.scatterplot(
{ name: "线性回归训练数据" },
{ values: xs.map((x, i) => ({x, y:ys[i]})) },
{xAxisDomain:[0,5],yAxisDomain:[0,9]}
);
const model = tf.sequential(); //创造一个连续模型
model.add(tf.layers.dense({units:1,inputShape:[1]})); //添加一个全连接层(点乘权重+偏置)
model.compile({loss:tf.losses.meanSquaredError,optimizer:tf.train.sgd(0.1)}); //设置:损失函数为均方误差MSE,优化器为随机梯度下降SGD,学习速率为0.1,学习率是一个需要调整优化的超参数
const inputs = tf.tensor(xs);
const labels = tf.tensor(ys);
await model.fit(inputs, labels,{
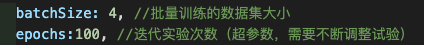
batchSize: 4, //批量训练的数据集大小(超参数,需要不断调整试验)
epochs:100, //迭代实验次数(超参数,需要不断调整试验)
callbacks:tfvis.show.fitCallbacks(
{name:'训练过程'},
['loss'],
)
});
};
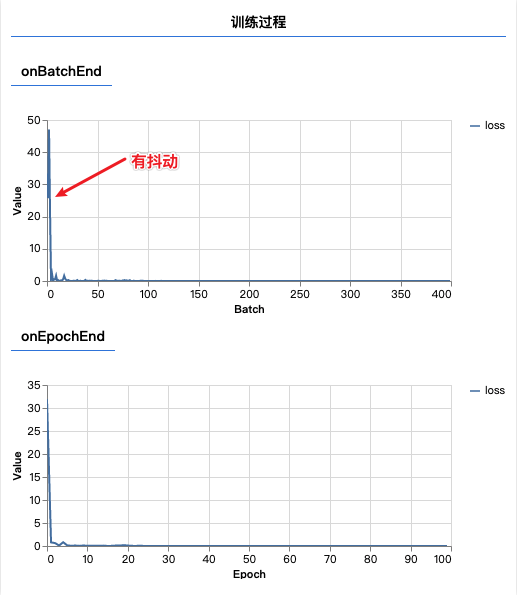
- 批量处理size设置为1,训练初期会有明显抖动

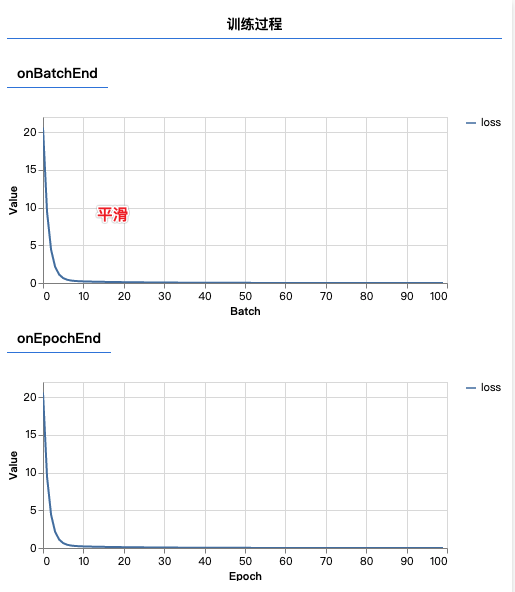
- 批量处理size设置为4,训练曲线比较平滑
进行预测
- 将待预测数据转为Tensor
- 用训练好的模型进行预测
- 将输出的Tensor转为普通数据并显示(模型的输入输出都是模型)
const output = model.predict(tf.tensor([5])); //将待预测数据5转为Tensor,用训练好的模型进行预测
output.print();
console.log(output.dataSync()); //将输出的Tensor转为普通数据并显示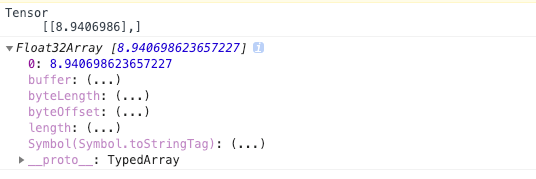
上次更新: